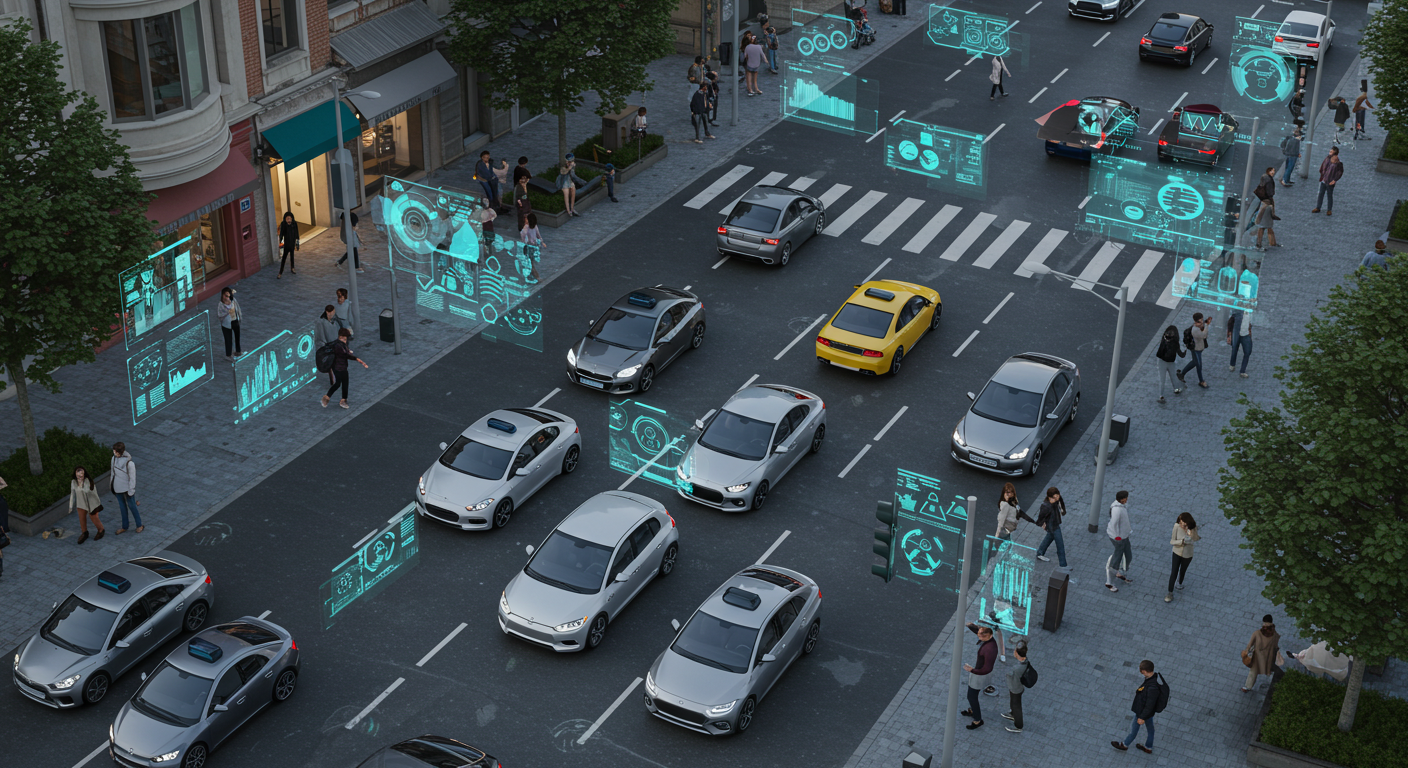
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has become one of the most transformative forces of the 21st century. Once confined to science fiction, AI now permeates nearly every aspect of modern life, from the way we work and communicate to how we shop, travel, and receive medical care. Its impact on society is profound, shaping industries, influencing culture, and raising ethical questions that challenge traditional values. As AI continues to evolve, its role will expand even further, making it one of the most significant drivers of change in the coming decades. This article explores the multifaceted impact of artificial intelligence on modern society, highlighting its benefits, challenges, and long-term implications.
Understanding Artificial Intelligence
Before diving into the effects of AI, it is essential to understand what it actually is. Artificial Intelligence refers to the development of computer systems capable of performing tasks that typically require human intelligence. These tasks include problem-solving, decision-making, speech recognition, language translation, and visual perception.
Types of AI
- Narrow AI (Weak AI): Specialized systems designed to perform specific tasks, such as recommendation engines on Netflix or voice assistants like Siri and Alexa.
- General AI (Strong AI): A theoretical concept where machines possess human-like cognitive abilities and can perform any intellectual task a human can.
- Superintelligent AI: A future possibility where machines surpass human intelligence, raising both excitement and concern among experts.
Currently, most applications involve narrow AI, but research is moving toward more sophisticated systems capable of learning and adapting autonomously.
AI in Everyday Life

Artificial Intelligence has seamlessly integrated into daily life, often in ways people don’t even notice. Its applications make routines more convenient, efficient, and personalized.
Smart Assistants and Homes
Voice-activated assistants like Google Assistant and Amazon Alexa have become household staples. They control lighting, regulate temperatures, answer questions, and even manage shopping lists. These systems not only save time but also enhance accessibility for people with disabilities.
Personalized Recommendations
Streaming services, e-commerce platforms, and social media sites leverage AI to analyze user behavior. This allows them to deliver personalized recommendations, increasing engagement and satisfaction. While convenient, it also sparks debates about privacy and the manipulation of consumer behavior.
Transportation
AI plays a central role in navigation apps, ride-sharing platforms, and the development of autonomous vehicles. Self-driving cars, though still in testing phases, promise to reduce accidents, improve traffic flow, and transform urban mobility.
AI in Healthcare
One of the most promising fields for AI application is healthcare. Its integration has the potential to revolutionize diagnosis, treatment, and patient care.
Disease Diagnosis
AI-powered systems can analyze medical images with incredible precision, often outperforming human radiologists. Early detection of cancers, heart conditions, and neurological disorders is becoming more accurate and accessible thanks to AI technologies.
Personalized Medicine
AI can analyze genetic data to create individualized treatment plans. This approach tailors therapies to the unique genetic makeup of each patient, improving outcomes and reducing side effects.
Healthcare Accessibility
In regions with limited access to doctors, AI chatbots and virtual health assistants provide preliminary diagnoses and medical advice, bridging healthcare gaps. Wearables that monitor vital signs in real time also empower patients to take control of their health.
AI and the Workforce

One of the most debated impacts of AI concerns employment. Automation and machine learning have the power to reshape industries, creating new opportunities while eliminating certain job roles.
Job Displacement
Repetitive tasks in manufacturing, customer service, and logistics are increasingly being handled by machines. This displacement has sparked fears of widespread unemployment, particularly in industries dependent on manual labor.
Job Creation
At the same time, AI generates new career opportunities. Roles in data science, AI ethics, cybersecurity, and machine learning engineering are in high demand. The challenge lies in retraining and reskilling workers to adapt to the changing landscape.
Human-AI Collaboration
Rather than replacing humans entirely, AI often augments human abilities. For example, doctors use AI to analyze scans faster, lawyers leverage AI to review contracts, and financial analysts rely on algorithms for predictive modeling. The future of work will likely focus on collaboration rather than replacement.
AI in Education
Education is another sector deeply influenced by artificial intelligence. From classrooms to online platforms, AI is reshaping how people learn and acquire knowledge.
Personalized Learning
AI systems can track student progress and adapt lessons to suit individual learning styles. This approach ensures that each student receives a customized experience, addressing weaknesses and building on strengths.
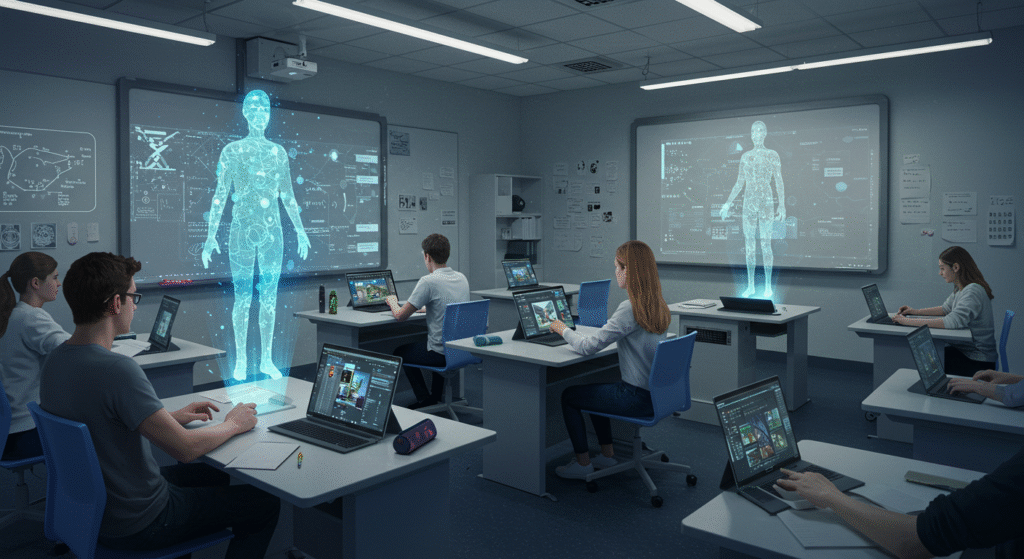
Virtual Tutors
AI-powered tutors provide additional support outside of classrooms. They are available 24/7, offering explanations, practice exercises, and feedback tailored to student needs.
Administrative Efficiency
AI also streamlines administrative tasks, such as grading assignments and managing schedules, freeing teachers to focus more on instruction and mentorship.
AI in Business and Industry
Companies across the globe are harnessing AI to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and innovate products and services.
Customer Service
AI-driven chatbots handle millions of customer queries daily. These bots can resolve simple issues quickly, allowing human agents to focus on complex problems. This not only improves customer satisfaction but also reduces operational costs.
Data Analytics
Businesses use AI to analyze vast amounts of data, uncovering insights that drive decision-making. Predictive analytics helps companies anticipate market trends, optimize supply chains, and develop strategies with greater precision.
Marketing and Advertising
AI personalizes advertising campaigns by analyzing consumer behavior. Dynamic pricing, targeted ads, and automated content generation are all powered by AI, increasing engagement and conversion rates.
AI in Governance and Security
Governments and security organizations are also leveraging AI, raising both opportunities and concerns.
Law Enforcement
AI tools assist in crime prevention, facial recognition, and predictive policing. While these systems enhance efficiency, they also spark debates about privacy, bias, and potential misuse.
National Security
AI plays a significant role in cybersecurity, monitoring threats, and responding to attacks faster than humans could. In military applications, AI is used for surveillance, drone control, and strategic planning.
Public Services
AI enhances public services by managing traffic flow, improving waste management, and optimizing energy distribution in smart cities. These applications contribute to sustainability and quality of life.
Ethical and Social Implications of AI
While the benefits of AI are vast, the technology also raises profound ethical questions that society must address.
Bias and Discrimination
AI systems learn from data, and if that data contains biases, the algorithms may perpetuate or even amplify them. This can lead to discrimination in hiring, lending, or law enforcement decisions.
Privacy Concerns
The use of AI in surveillance, data collection, and behavioral analysis raises serious privacy issues. Striking a balance between innovation and individual rights will be a key challenge moving forward.
Dependence on Technology
As society becomes increasingly reliant on AI, questions about human agency and control arise. Overreliance could lead to a loss of critical thinking skills and diminished human decision-making authority.
The Future of Humanity
Discussions around Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) and superintelligence raise philosophical questions: If machines surpass human intelligence, what will humanity’s role be? Ensuring alignment between AI’s goals and human values is crucial for a safe future.
The Positive Outlook
Despite the challenges, the potential of AI to improve human life is immense. From curing diseases to reducing poverty, AI could be the catalyst for solving some of the world’s most pressing problems.
Sustainable Development
AI can optimize energy use, improve agricultural yields, and combat climate change through predictive modeling and resource management. Its role in sustainability efforts will be critical in the coming decades.
Global Connectivity
AI-driven technologies expand access to education, healthcare, and communication, especially in underserved areas. This connectivity fosters global collaboration and inclusivity.
Human Enhancement
By augmenting human abilities, AI could enable people to achieve more than ever before. From medical implants to brain-computer interfaces, AI is not just transforming society but redefining what it means to be human.

Conclusion: Navigating an AI-Driven Future
The impact of artificial intelligence on modern society is undeniable. It enhances convenience, improves healthcare, revolutionizes industries, and connects the world in unprecedented ways. At the same time, it presents challenges that demand thoughtful regulation, ethical oversight, and public dialogue. The future of AI is not just a technological question but a human one: how will we, as a society, choose to integrate and govern this powerful force?
AI has the potential to be humanity’s greatest tool for progress—or its most dangerous invention if mismanaged. Navigating this future requires balance, foresight, and a collective commitment to ensuring AI serves the greater good. One thing is certain: artificial intelligence is no longer a distant dream; it is the reality shaping our modern world, and its influence will only deepen in the years to come.